spring devtools
用于开发时即时编译和刷新。
安装
Maven.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Gradle.
dependencies {
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-devtools")
}
注意事项
- 运行打包好的可执行程序,如java -jar xxx.jar时,devtools不运行,它认为这时是生产环境
- 为防止devtools被传递给使用的模块的其他工程,可以在maven中设置optional,或是gradle中设置compileOnly
- 重新打包发布的时候devtools不会包含在里面,要是想使用它的远程调试功能,需要设置excludeDevtools为关闭状态。这样就可以包含了。
缓存功能的开启和关闭
正常是在application.properties中设置,但使用了devtools就需要设置了,devtools会自动判断是研发还是生产环境,并自动设置这些项。 比如:spring.thymeleaf.cache
支持的有:
- FreeMarker
- Groovy
- Thymeleaf
- Mustache
完整支持列表见: https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/blob/v2.0.2.RELEASE/spring-boot-project/spring-boot-devtools/src/main/java/org/springframework/boot/devtools/env/DevToolsPropertyDefaultsPostProcessor.java
自动重启
classpath内的文件变动就会触发重启,devtools通过重启使变动生效。但资源文件变动不触动重启,他们只需要不缓存就行了。
Triggering a restart
As DevTools monitors classpath resources, the only way to trigger a restart is to update the classpath. The way in which you cause the classpath to be updated depends on the IDE that you are using. In Eclipse, saving a modified file causes the classpath to be updated and triggers a restart. In IntelliJ IDEA, building the project (Build -> Build Project) has the same effect.
版本
http://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/org/springframework/boot/spring-boot-devtools/
没读完: http://www.cnblogs.com/java-zhao/p/5502398.html http://ju.outofmemory.cn/entry/241222
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/using-boot-devtools.html
spring boot项目如何在生产环境和研发环境使用不同的数据库?
理想的做法是研发和生产环境分别使用sqlite3和mysql。 或都使用H2
使用H2的时候可以以文件方式使用,也可以以内存的方式使用。我选择文件方式,这样可以取生产环境的一个数据库快照给研发环境测试用。
halo的配置
spring:
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
# H2database 配置
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
url: jdbc:h2:file:~/halo/halo
username: admin
password: 123456
h2:
console:
settings:
web-allow-others: true
path: /h2-console
enabled: true
可以看到生成的数据库文件是:
➜ zhangfuwen ls ~/halo/halo.mv.db
/Users/dean/halo/halo.mv.db
h2的配置参考
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000007002140
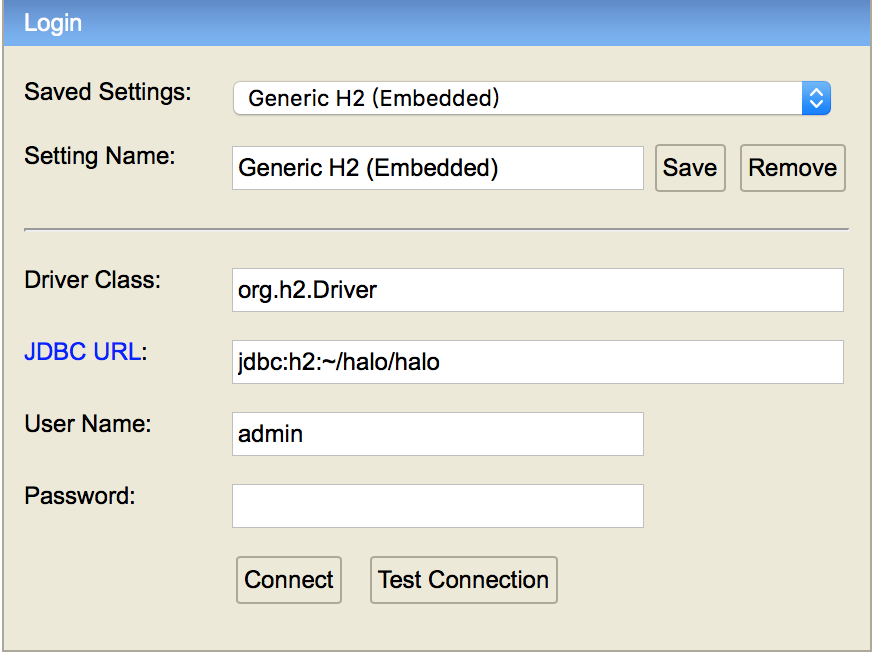
h2-console的登陆方法
JPA 与Hibernate的关系
Hibernate ORM是JPA规范的一个实现。
JPA即Java Persistence API,它定义了一组ORM必须实现的接口。 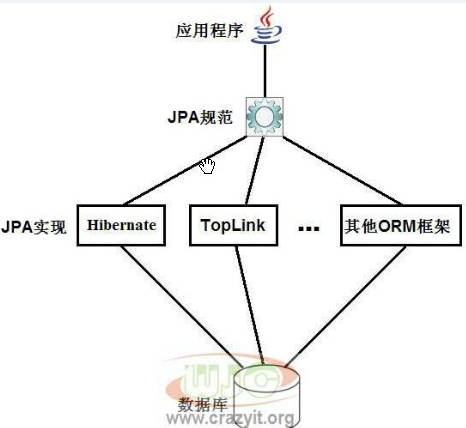
一些其他的JPA配置
#JPA Configuration:
spring.jpa.database=MYSQL
# Show or not log for each sql query
spring.jpa.show-sql=false
spring.jpa.generate-ddl=true
# Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, update)
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create
#spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming_strategy=org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy
#spring.jpa.database=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
application.properties中配置的tomcat
这个配置是怎么对tomcat起作用的? 里面embed了tomcat,如果不想embed tomcat应该怎么做,在哪里配置tomcat?
在内置tomcat的情况下,是spring实例化一个tomcat类,并调用setter把properties文件的内容设置进去,但是外置的情况下是怎么配置的呢?通过war。在war包的情况下,是war包要遵循tomcat的规则,在固定位置写对应格式的配置文件。在application.properties里写还管用吗?
可以参考的文章:
http://www.chinacion.cn/article/1148.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/ad102217ac6c
maven project to gradle project
gradle init --type pom