levenshtein-distance
利文斯坦 距离 简要来说:
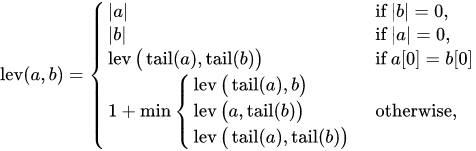
- b是空串,距离就是a的长度,反之亦然
- a[0] == b[0] ,则lev(a,b ) = lev(a[1:], b[1:]),即首字符相同,则忽略不计
- 如果a[0] != b[0],则计1,再+下面三个值的最小值:
- lev(a[1:], b)
- lev(a, b[1:])
- lev(a[1:], b[1:])
听起来很简单,可以写代码了,
int lev(std::string_view a, std::string_view b) {
if(a.empty() || b.empty()) {
return a.size() + b.size();
}
if(a[0] == b[0]) {
return lev(a.substr(1), a.substr(1));
} else {
int sub1 = lev(a.substr(1), b);
int sub2 = lev(a.substr(1), b.substr(1));
int sub3 = lev(a, b.substr(1));
return 1 + std::min({sub1, sub2, sub3});
}
}
如何用于搜索
const float limit = 0.5;
std::string s = "history";
std::string term = "hitory";
bool match(std::string &s, std::string & term) {
return (float)lev(s, term)/ term.size() < limit;
}
优化
实际试用了下,发现效率超级低,用于搜索app名字都被导致卡顿和风扇狂转。
最简单的优化就是超过一定距离后放弃。比如说超过搜索term长度一半的时候。